Fleet Vehicle Management: Best Practices to Optimize Your Operations
Fleet vehicle management isn’t just about keeping a set of vehicles on the road—it’s about running a smarter, safer, and more efficient operation....
Keep an eye on the road
Simplify your driver's routine
For efficient decision making
Ensure the compliance of your fleet
Simplify the daily life of your drivers
Maximize the value of your data
Unparalleled monitoring of your assets
The friendly competition that pays off
Planning powered by data
Exceed your customers' expectations
Provide better service to your users
Maximize the satisfaction of your citizens
Simplify your daily life on the construction site
Facilitate the electrification of your fleet
Our experts meet your needs
Easily meet the standards
Improve the safety of your drivers
Protect your data and your fleet
7 min read
Miguel Lage
Nov 6, 2023 10:59:13 AM
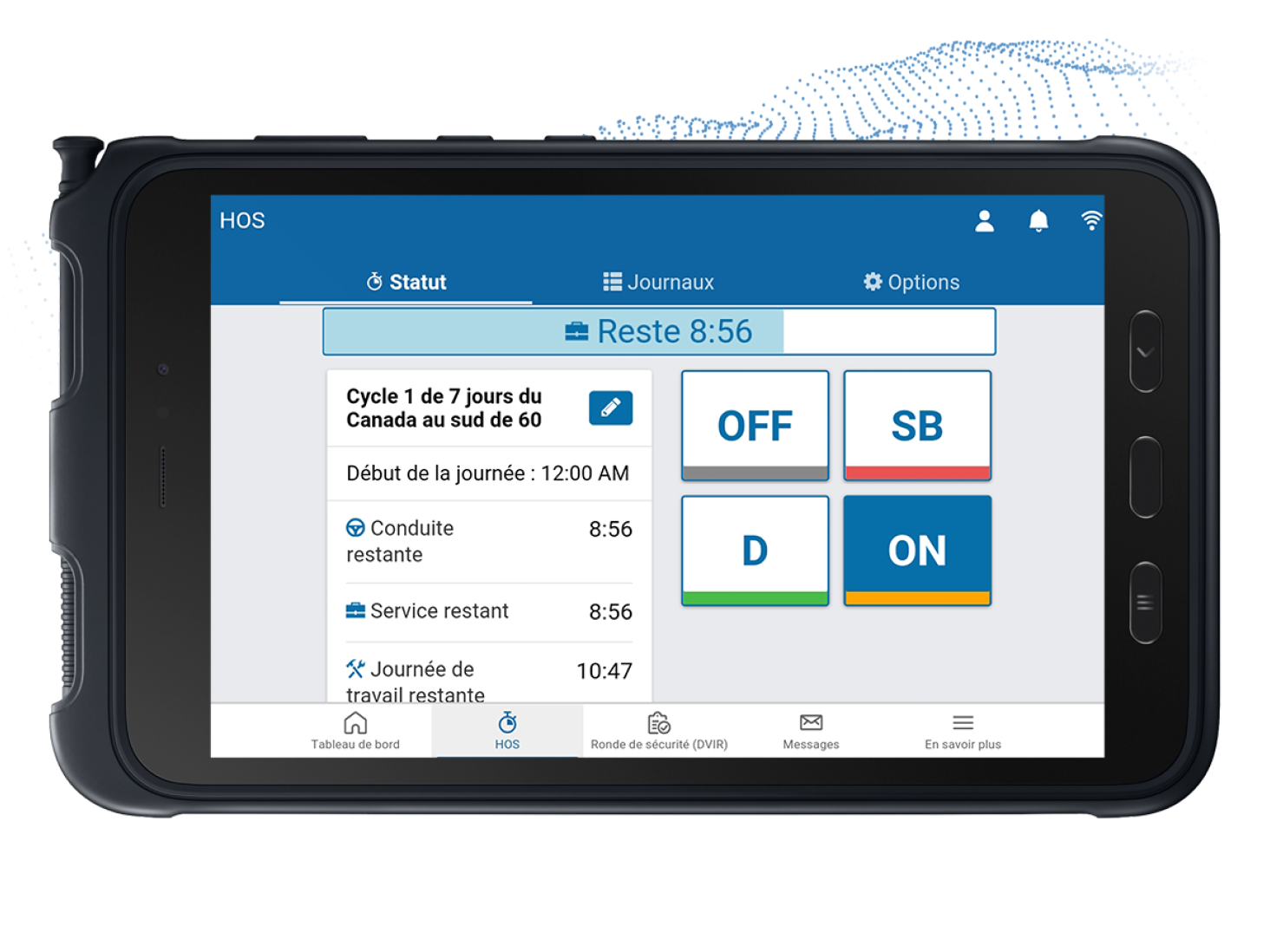
Canada's economy heavily relies on the trucking industry, which connects various provinces and territories through a network of goods and services. In this activity, the Hours of Service (HOS) rules are crucial in ensuring safety and compliance. It ensures that the wheels of commerce are in sync with the well-being of those behind the wheel.
As a fleet manager, navigating the complex Canadian HOS regulations can be challenging. That's why we've created this guide to help you understand daily and shift limitations, regional variations, and the shift to Electronic Logging Devices (ELDs). We will provide the insights and tools you need to achieve compliance, ensure safety, and maintain operational excellence in the Canadian trucking industry.
The HOS rules govern drivers' working hours in commercial motor vehicle (CMV) operations. They serve as a balance between the demands of the industry and the health and safety of the drivers. These rules are enforced by national governing bodies, ensuring a uniform standard across the vast expanse of Canada.
The Ministry of Transport plays a crucial role in the implementation and supervision of electronic lockout devices (ELDs), ensuring compliance with current regulations.
To fully understand the present by-law, it is crucial to master certain key definitions:
These regulations apply to all commercial vehicles operating in Canada, whether they are used to transport people or goods. This includes a wide range of vehicles, from trucks to buses to passenger vehicles.
The regulations also apply to commercial vehicle drivers working for motor carriers or shippers. All players in the transport industry must understand and comply with these rules to ensure the safety and efficiency of transport operations across the country.
The Canadian Hours of Service regulations are anchored in detailed daily and shift limitations that govern the operational parameters for commercial motor vehicle drivers. These limitations are meticulously crafted to balance the demanding schedules of the trucking industry and the imperative need for driver safety and well-being.
Beyond just driving, the on-duty limits encompass all the time a driver spends performing work-related tasks, including vehicle maintenance, loading and unloading cargo, and paperwork. These limits are designed to prevent the cumulative fatigue that can arise from long work hours, whether behind the wheel or not.
The shift or workday limits consider the broader picture of a driver's work schedule. These limits define the maximum allowable hours a driver can be on duty, including driving time, over an extended period, often referred to as a "shift" or "workday." This ensures drivers have sufficient off-duty time to rest and recover between shifts.
Central to the HOS regulations is the off-duty compulsory time. This is a non-negotiable period during which drivers must be free from all work-related activities. It's structured to give drivers uninterrupted rest, allowing them to recharge fully before starting their next shift. This off-duty time is not just a pause in work; it's a crucial period for maintaining the long-term health and alertness of drivers.
Canada's Hours of Service regulations have unique features tailored to the trucking industry's specific needs. These regulations include a provision for off-duty deferrals, specific requirements for adverse driving conditions, and unique treatment of the North. These features demonstrate a regulatory framework that prioritizes safety and acknowledges the diverse challenges of the trucking industry while providing practical solutions to support the efficient and safe operation of commercial motor vehicles across the nation.
HOS cycles are predefined periods during which drivers must follow specific limits on driving and on-duty time, followed by an off-duty period to reset the cycle. They are essential to prevent cumulative fatigue, a significant risk factor for drivers who spend extended periods on the road. Drivers and fleet managers must understand and manage these cycles to maintain compliance, safety, and efficiency in Canada's trucking operations. HOS cycles impact route planning, load scheduling, and supply chain dynamics and are a cornerstone of the trucking industry's operational rhythm.
The Canadian Hours of Service regulations offer provisions for splitting off-duty time and utilizing sleeper berths, reflecting an understanding of CMV drivers' diverse needs and realities. These provisions offer flexibility while ensuring drivers receive the rest they need to operate safely and efficiently.
The HOS regulations allow drivers to split their required off-duty time into separate periods, provided that certain conditions are met. This flexibility is crucial for drivers who cannot take an extended continuous break due to operational demands or personal preferences. By splitting off-duty time, drivers can tailor their rest periods to better align with their natural sleep patterns or the specific needs of their routes.
For drivers who operate vehicles equipped with sleeper berths, the HOS regulations provide specific provisions that allow a portion of the required off-duty time to be spent in the sleeper berth. This is particularly beneficial for long-haul drivers who spend several days on the road. The sleeper berth provisions enable drivers to rest effectively without seeking accommodations outside their vehicle, thus maintaining the continuity of their operations.
The trucking industries in Canada and the United States are closely connected, but their Hours of Service regulations differ nuancedly.
This includes differences in the structure of HOS cycles, provisions for adverse driving conditions, treatment of off-duty time and sleeper berths, and the approach to ELDs.
A comparative analysis of these rules is essential for anyone involved in cross-border trucking operations to ensure compliance, better planning, and safer and more efficient transportation across North America.
Personal conveyance refers to using a CMV for personal purposes outside commercial operations. Both Canada and the U.S. allow personal conveyance, but the specific rules can differ. In Canada, drivers can use their CMVs for personal reasons as long as they're off-duty. The U.S. Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) also provides guidelines to ensure safety isn't compromised. However, nuances exist in how personal conveyance is interpreted and enforced in each country, such as allowable distance, documentation requirements, and the impact of resetting HOS cycles. Drivers and fleet managers across the U.S.-Canada border should understand these differences to maintain compliance and safeguard safety and well-being.
Canada's trucking industry has transitioned from traditional paper logbooks to Electronic Logging Devices. ELDs automatically record driving time, reducing errors, promoting fair competition, and enhancing road safety. For drivers, ELDs provide a less time-consuming way to record hours, and for carriers, they offer a more efficient way to monitor compliance and optimize operations. This shift reflects a commitment to leveraging technology to streamline operations, enhance compliance, and improve safety in the industry.
Canada's ELD mandate is a significant regulatory change for the trucking industry. It requires most commercial motor vehicle drivers to use a certified ELD by Transport Canada for recording hours of service to improve compliance with Hours of Service regulations and road safety. However, some drivers and operations are exempt from the ELD mandate. Compliance involves understanding the device's functionality and training drivers on its use. As the industry embraces this shift, the ELD mandate is a testament to Canada's commitment to safety and regulatory adherence.
Navigating the intricate world of transportation compliance can be daunting, but AttriX is a trusted name you can rely on. Our ELD solution, powered by Geotab, is a certified and registered system designed to ensure your fleet adheres to the strict Hours of Service regulations set by Transport Canada and the FMCSA. With our innovative and reliable ELD solution, you can rest assured that your fleet is always compliant, minimizing the risk of costly violations and penalties.
Here's how AttriX can be instrumental in streamlining your compliance processes:
AttriX provides a comprehensive, integrated, simple, and secure solution to ensure your fleet's compliance, offering peace of mind and a competitive edge in the transportation industry.
Navigating the Canadian Hours of Service regulations is a complex yet crucial aspect of managing a compliant and efficient trucking operation. Here are the key takeaways from our comprehensive guide:
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the Canadian HOS regulations and their implications is indispensable for the smooth operation of the trucking industry. Compliance with these regulations ensures the safety of drivers and other road users and enhances the transportation network's efficiency and reliability, which is vital to Canada's economy.

Fleet vehicle management isn’t just about keeping a set of vehicles on the road—it’s about running a smarter, safer, and more efficient operation....

Let’s face it—running a fleet today isn’t as simple as keeping track of vehicles on a map. The expectations are higher, the pace is faster, and the...

By Anthony Mainville, CEO - Attrix Technologies. If there was one panel that cut through the aspirational rhetoric at ACT Expo 2025 to deliver...